INFO 4120/6120 Ubiquitous Computing Group Project
Low-voice Whisper Recognition on Smartwatch
Overview
We designed and prototyped a smartwatch-based silent speech interface that recognizes whispered commands using ultrasonic active acoustic sensing. Unlike prior work on eyewear-based systems (e.g., EchoSpeech), our project reimagines silent speech recognition from the wrist — a ubiquitous and socially acceptable wearable form factor.
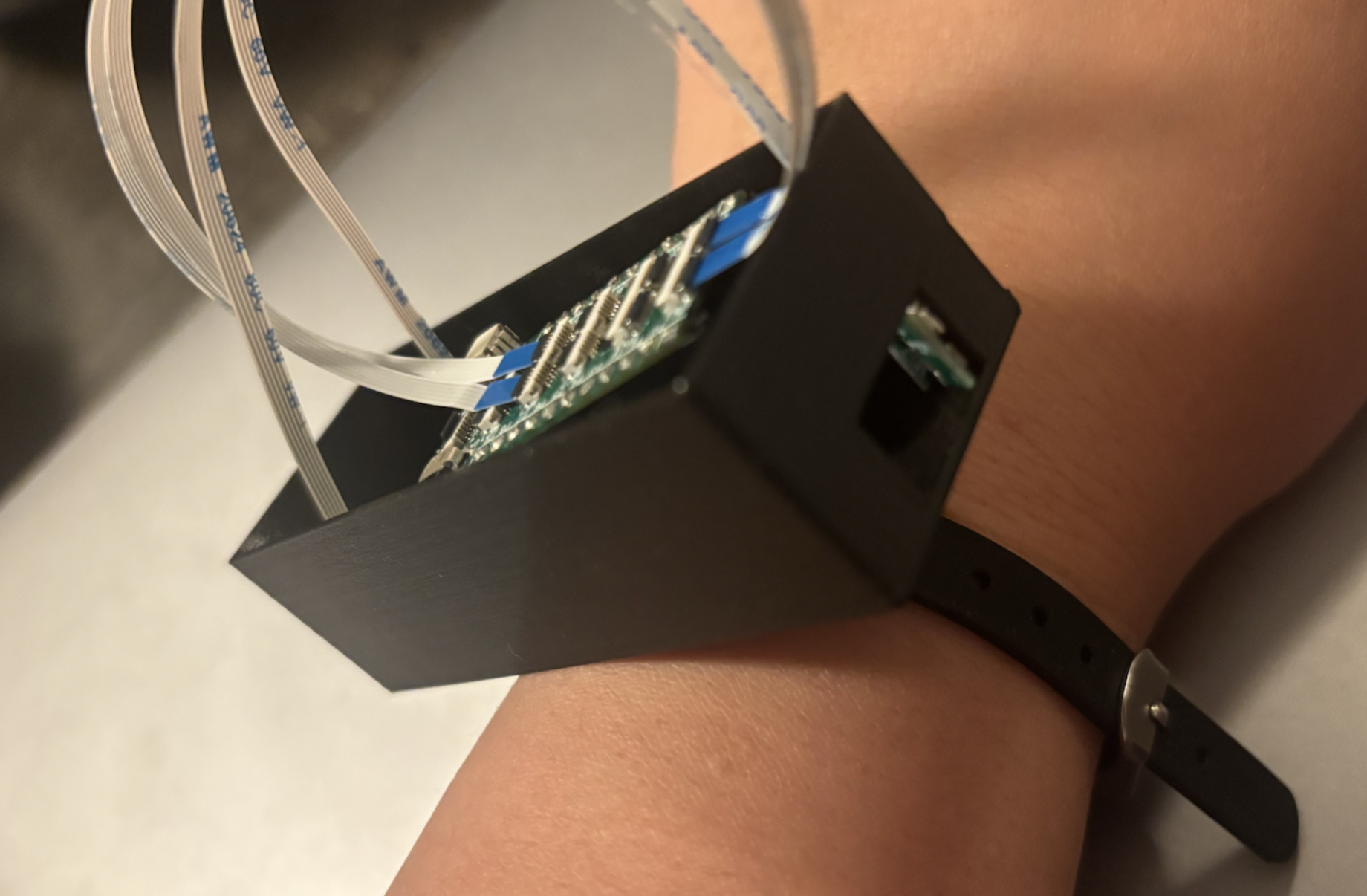
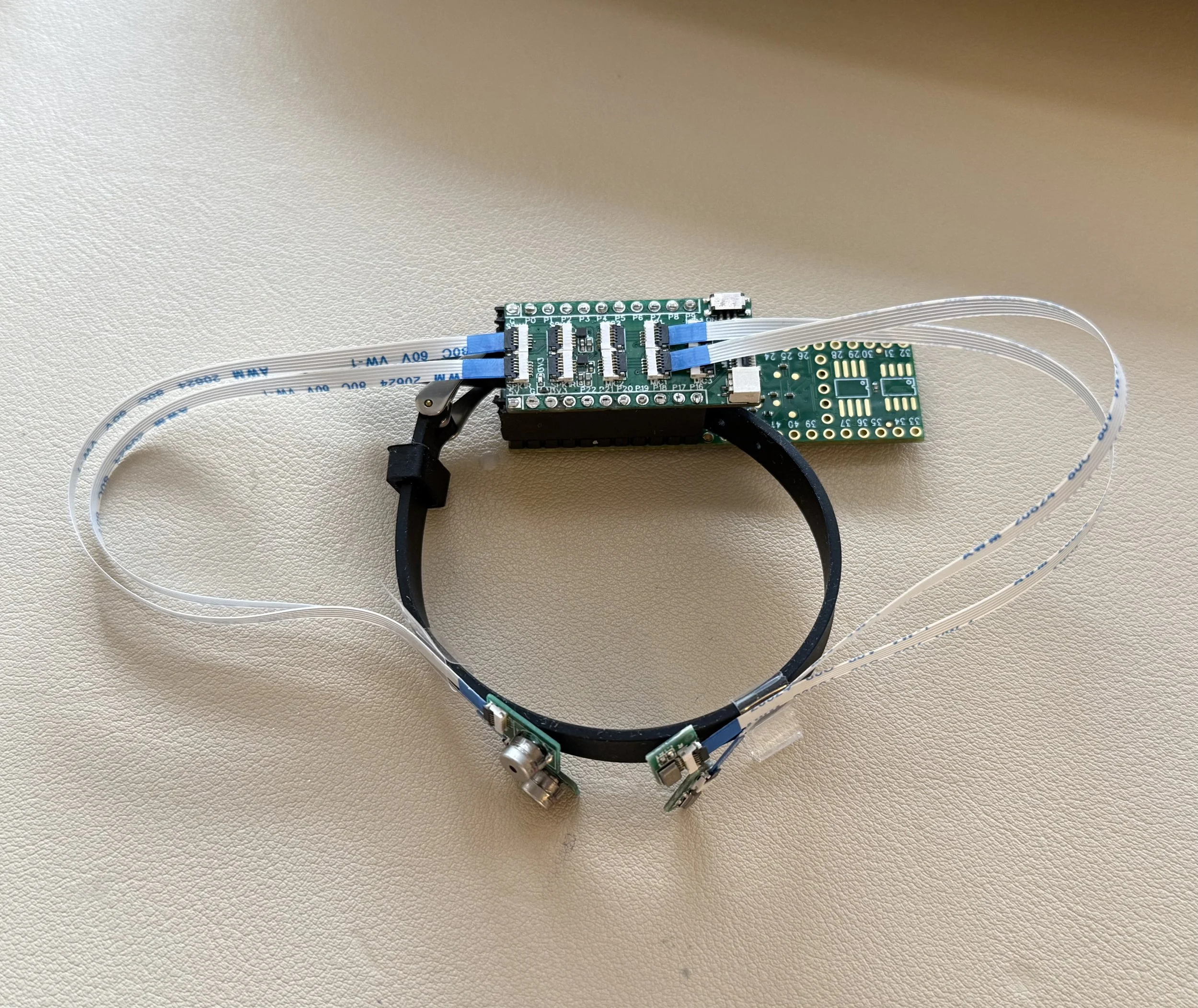
Our prototype integrates ultrasonic speakers, microphones, and a Teensy 4.1 microcontroller in a custom 3D-printed watch enclosure. Using deep learning (ResNet-18 backbone), we classified echo profiles of lip movements corresponding to 29 everyday commands (digits, media control, wake words, authentication phrases).
Why It Matters
Privacy & Discretion: Enables communication without audible speech, useful in noise-sensitive or socially constrained settings.
Accessibility: Supports users with vocal impairments or fatigue.
Ubiquity: Brings silent speech recognition to smartwatches, already part of daily life.
System Design & Methodology
Hardware Prototyping
Two ultrasonic speakers + two microphones in a wrist-mounted enclosure, logging echo signals to a microSD card.
Data & Methods
Command Set: 29 phrases, including digits, wake words (“Hey Siri,” “Alexa”), and authentication (“Verify me,” “Confirm identity”).
Participants: 4 native English speakers, 6,380 utterances collected.
Echo Profiles: Captured via frequency-modulated continuous waves, visualized to reveal consistent stripe patterns tied to lip motions.
Key Results
*
Key Results *
Model: ResNet-18 adapted for 4-channel echo input.
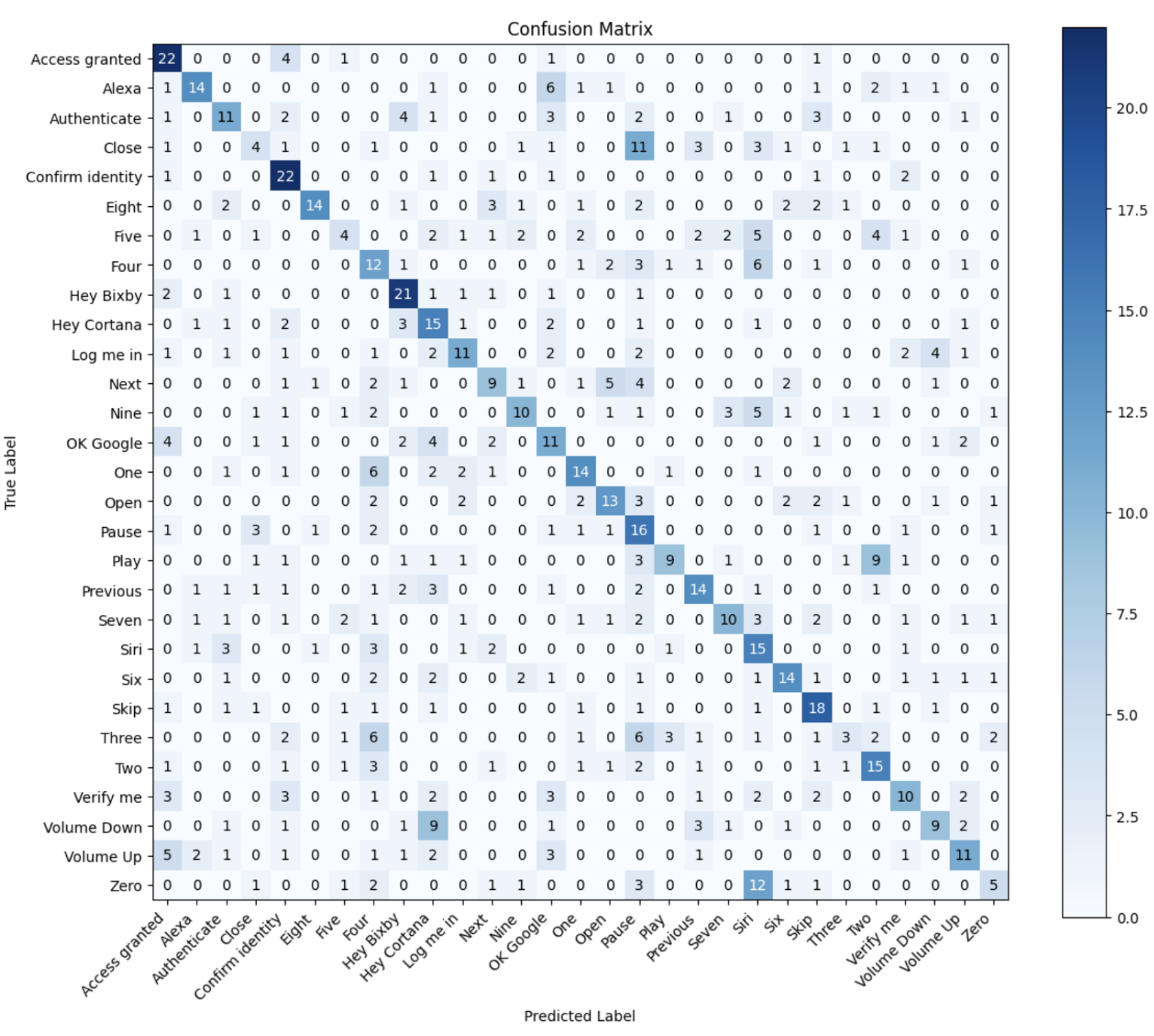
Performance:
One-channel input: 43% accuracy, F1 = 0.42
Four-channel input: 55% accuracy, F1 = 0.56
Best performing commands: “Hey Bixby,” “Verify Me,” “Open” (recall up to 72%).
Future Directions
Larger, more diverse participant studies in real-world conditions.
Improved form factor with flexible PCB arrays and better microphones.
Hybrid cloud-edge training pipelines for better models.
Exploring larger architectures (ResNet-50, Transformers).
Longitudinal field study for usability and social acceptability.
Limitations
Small participant pool (N=4, ages 22–24).
Confusion among acoustically similar words (e.g., “Zero” vs “Three”).
Hardware fragility and motion artifacts from wrist placement.
Evaluation only in quiet lab conditions.